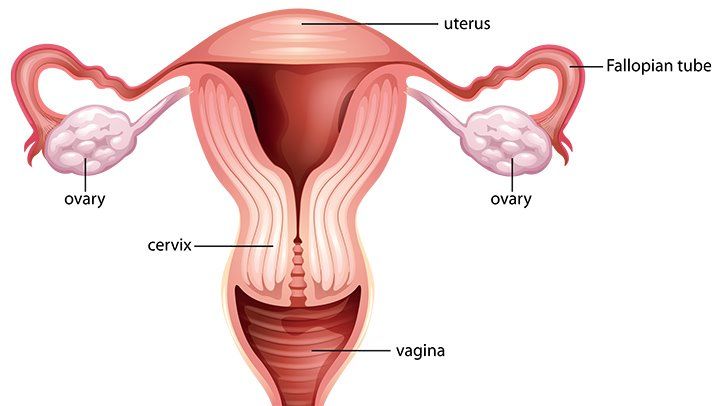
The female reproductive system is far more complex and delicate than the male reproductive system. This makes it susceptible to medical disorders based on its complexity. One such disorder is Endometriosis. In normal terms, it is a condition where the normal tissue that forms the uterus’s inside female anatomy lining grows in places where it isn’t meant to.
This disorder commonly occurs when endometrial-like tissue grows on the ovaries, bowel, and pelvis. After this build-up of tissue in unusual places, the hormonal change of a normal menstrual cycle affects female anatomy these tissues and causes break down in these tissues.
In short, these unusual tissues also undergo the same process of growth, thicken and breakdown as the endometrium during the menstrual cycle.
Why the pain?
Unlike in the menstrual cycle, there is no place of discharge for the tissues growing in unusual places, so over time, these broken-down tissues become trapped in the pelvis.
The trapped tissue in the pelvic region can cause irritation, scar formation, adhesions, severe pain during periods, and fertility problems.
Symptoms – Should you be concerned?
Endometriosis has varying symptoms. Some women have mild symptoms, whereas others can have severe or moderate symptoms. The degree of the symptoms in this disorder does not correspond to the severity of the stage or condition of the disorder.
Pelvic pain is the most common symptom. Apart from this, the symptoms can be :
- Painful periods
- Lower abdomen pain before, during, or after periods
- Pain after sexual intercourse
- Infertility
- One or two weeks cramps around periods
- Discomfort with bowel movements.
It also may be asymptomatic in some cases, so periodic gynaecological visits can be helpful.
Treatment
The severe symptoms can destroy a person’s day-to-day life if left untreated. Endometriosis is not curable, but its symptoms can be treated.
There is a complex array of treatments available to treat and manage the symptoms. A consultation with a dynamic is necessary to decide the severity and the optimal treatment for the condition. The basic medication for symptoms is over-the-counter pain medications, though many of the times, female anatomy this may not suffice to suppress the symptoms.
Hormone therapy: Consumption of supplemental hormones can help keep the pain at bay and stop the state of endometriosis.
Hormonal Contraceptives: These are birth control pills, patches, and vaginal rings which can reduce or even stop the pain in less severe cases of endometriosis. Hormonal contraceptives decrease the rate of endometriosis by preventing the monthly growth of endometrial tissue.
GnRH agonists and antagonists: Taking GnRH or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists stops the production of estrogen. Estrogen is the hormone that determines female sexual characteristics; stopping the production of estrogen would induce artificial menopause and stop menstruation.
Conservative surgery: This is a surgery to remove all the abnormal growth in the woman. It is mostly done if hormonal treatments fail to work on the woman or if she wants to get pregnant.
Endometriosis and emotions
Being diagnosed and living with Endometriosis can affect a person’s mental and emotional health. The reaction to the diagnosis and the thought of learning to live with it for their entire life can cause feelings of sadness, depression, and anxiety.
During this time, it’s important to know that normal life is possible with the right treatment and that it’s not embarrassing in any way to have this condition.
Many Endometriosis support groups help women feel comfortable about themselves. Apart from this, visiting a psychologist can help relieve women of their insecurities about themselves during this emotionally challenging time.